Have an appointment? Complete the Intake Form
Top Causes Behind Swollen Gums and How to Address Them
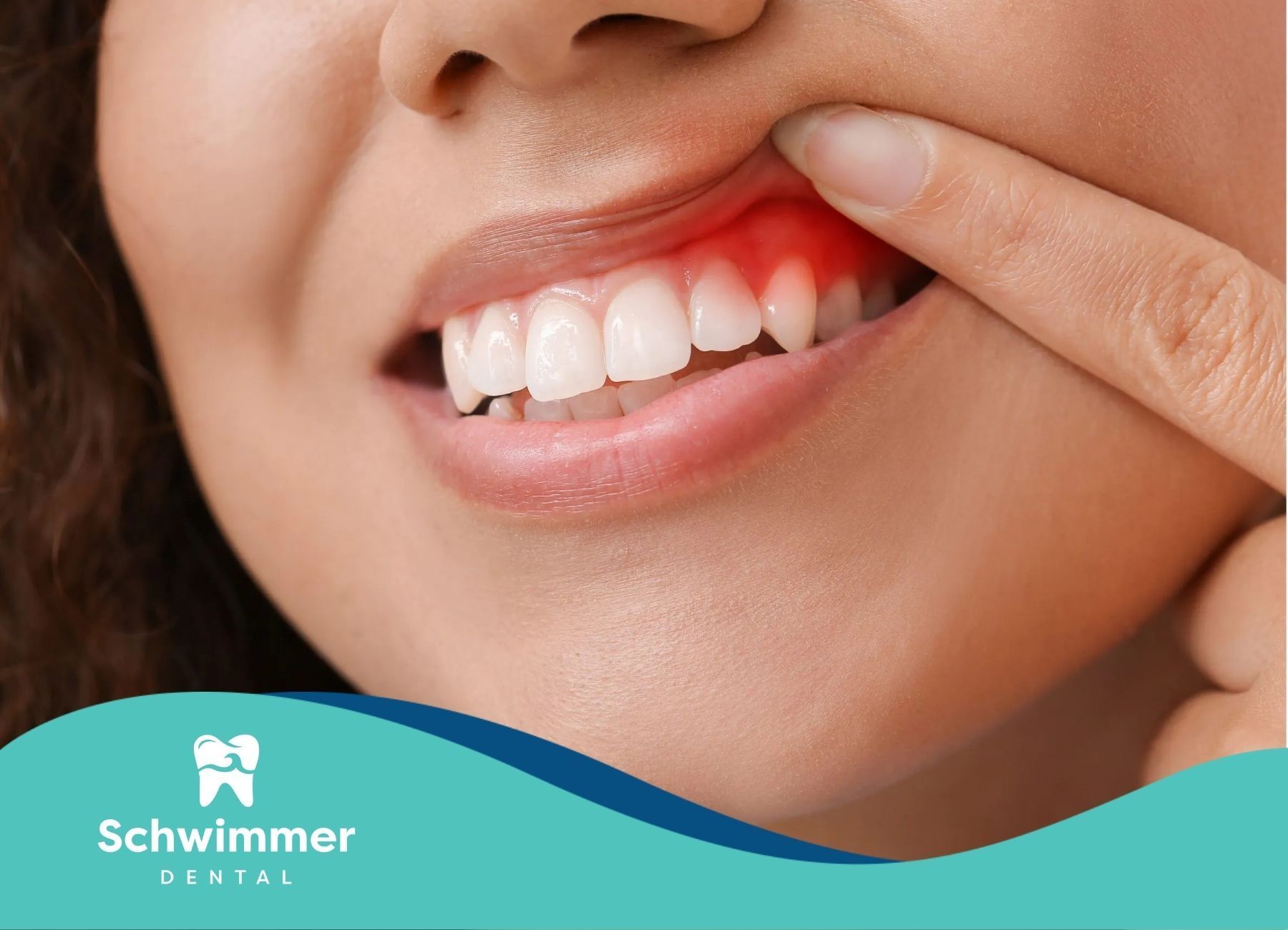
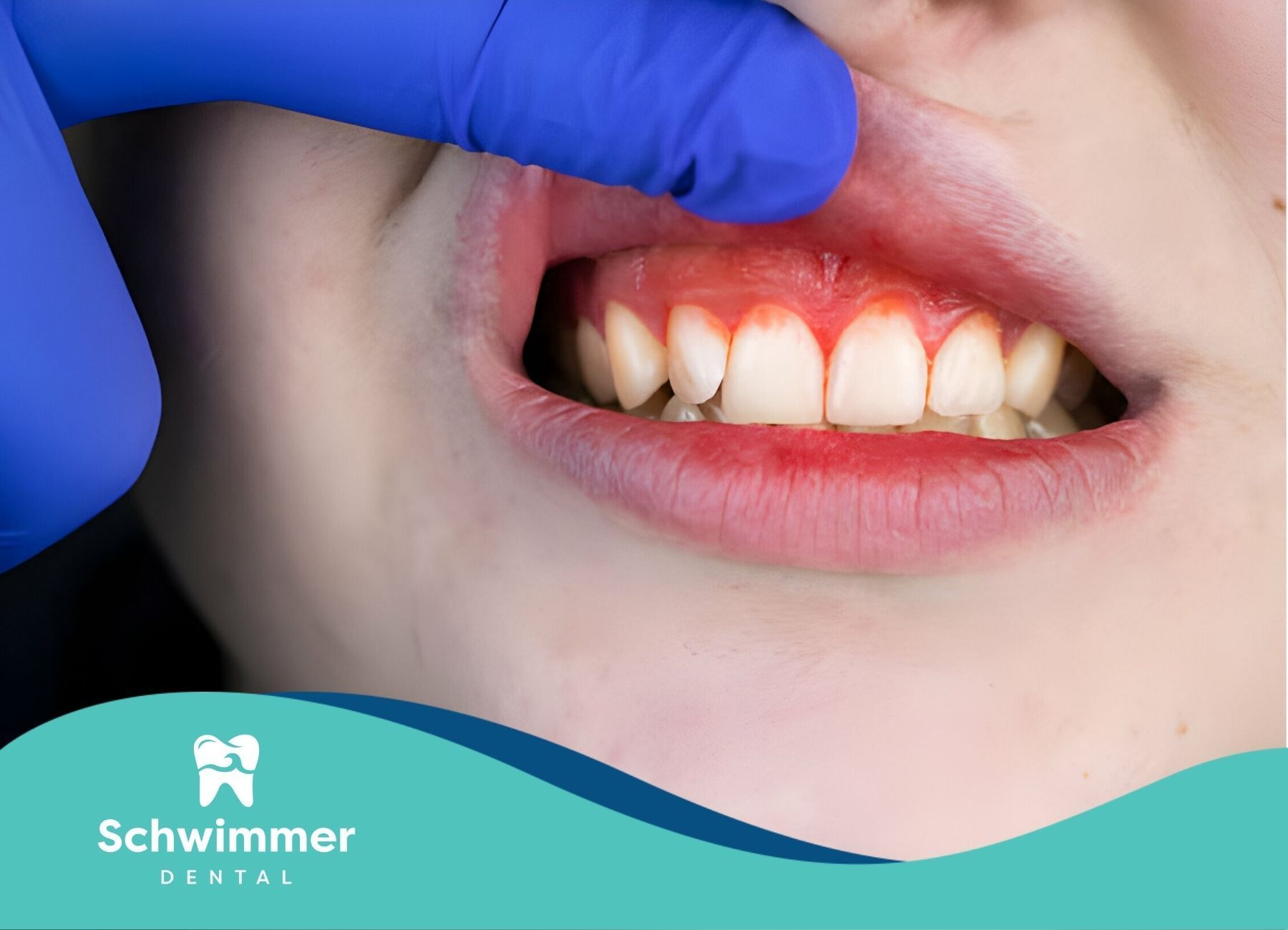
Understanding Swollen Gums
Definition of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums, also known as gingival swelling, are a common oral health issue characterized by an increase in the size of the gums. This condition often results in gums that appear red or purplish, smooth, and shiny due to increased blood flow. Swollen gums can be a symptom of various underlying issues, including gingivitis, infections, vitamin deficiencies, or hormonal changes.
Importance of Addressing Swollen Gums
Addressing swollen gums promptly is crucial for maintaining overall oral health. If left untreated, swollen gums can lead to more severe dental problems, such as periodontitis, tooth loss, and infections. Additionally, swollen gums can be indicative of other health conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, which require medical attention.
Prompt treatment for swollen gums is recommended to prevent issues from worsening. Common dental treatments include deep cleaning, root canal therapy, or tooth extraction. If swollen gums persist for more than two weeks, it is advisable to seek professional dental care. Severe pain that does not improve with medication should prompt immediate dental care.
For more information on the causes of swollen gums, visit our article on reasons for swollen gums. If you are experiencing swollen gums around a specific tooth, you may find our guide on swollen gums around tooth helpful. Additionally, for home remedies to alleviate swollen gums, check out our article on swollen gums home remedies.
Common Causes of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums can be a sign of various underlying issues. Understanding the common causes can help in addressing and preventing this condition effectively.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene is one of the primary causes of swollen gums. When plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates on the teeth and gums, it can lead to inflammation and swelling. Regular brushing and flossing are essential to remove plaque and maintain healthy gums. Neglecting these practices can result in gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a significant cause of swollen gums. It progresses in stages, starting with gingivitis and potentially advancing to periodontitis if left untreated. Gingivitis causes the gums to become red, swollen, and prone to bleeding. If it progresses to periodontitis, the inflammation can lead to the destruction of the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone.
| Stage of Gum Disease | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Red, swollen gums, bleeding during brushing or flossing |
| Periodontitis | Receding gums, persistent bad breath, loose teeth |
For more information on the symptoms and characteristics of swollen gums, visit our article on swollen gums and bleeding.
Infections and Inflammation
Infections and inflammation can also cause swollen gums. Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to gum inflammation. For instance, a common viral infection like herpes can cause acute herpetic gingivostomatitis, leading to swollen and painful gums. Additionally, conditions such as abscesses or tooth infections can result in localized gum swelling around the affected tooth.
| Type of Infection | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Bacterial | Red, swollen gums, pus, bad taste in mouth |
| Viral | Painful sores, swollen gums, fever |
| Fungal | White patches, redness, swelling |
Understanding the common causes of swollen gums is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Regular dental checkups and maintaining good oral hygiene can help prevent many of these issues. If you experience persistent gum swelling, it is advisable to seek professional dental care to address the underlying cause.
Health Conditions Linked to Swollen Gums
Swollen gums can be a symptom of various underlying health conditions. Understanding these connections is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Here, we explore the links between swollen gums and systemic diseases such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and other conditions.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body's ability to process blood sugar. It can have a significant impact on oral health, including causing swollen gums. People with diabetes are
more susceptible to infections, including gum infections, due to their compromised immune system. High blood sugar levels can also contribute to the development of gum disease, which can lead to swelling, bleeding, and sensitivity.
| Health Condition | Impact on Gums |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | Increased risk of infections, gum disease, and inflammation |
HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS is another condition that can lead to swollen gums. The virus weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections, including those in the mouth. People with HIV/AIDS are at a higher risk of developing gum diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis, which can cause significant gum swelling and discomfort.
| Health Condition | Impact on Gums |
|---|---|
| HIV/AIDS | Higher susceptibility to gum infections and diseases |
Other Systemic Diseases
Several other systemic diseases can also contribute to swollen gums.
Chronic inflammation, which is common in conditions such as heart disease, obesity, and autoimmune disorders, can exacerbate gum problems. Additionally, untreated gum disease can be linked to respiratory disease, coronary artery disease, stroke, and rheumatoid arthritis.
| Health Condition | Impact on Gums |
|---|---|
| Heart Disease | Increased inflammation and risk of gum disease |
| Obesity | Higher likelihood of chronic inflammation affecting gums |
| Autoimmune Disorders | Compromised immune response leading to gum issues |
Understanding the connection between these systemic diseases and swollen gums is essential for comprehensive oral care. Regular dental checkups and maintaining good oral hygiene can help manage and prevent gum problems.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Swollen Gums
Appearance of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums often exhibit noticeable changes in appearance. They usually have a reddish or purplish hue due to increased blood flow and may appear smooth or shiny. These visual changes are often accompanied by swelling, making the gums look puffy and enlarged. The color and texture changes are key indicators of underlying issues such as gingivitis or periodontal disease.
Bleeding and Sensitivity
Bleeding and sensitivity are common symptoms associated with swollen gums. Swollen gums tend to bleed easily, especially during activities like brushing or flossing. This bleeding is often a sign of inflammation and can be an early indicator of gum disease. In addition to bleeding, swollen gums can be tender to the touch and may cause discomfort when eating or drinking.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Bleeding | Gums bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing |
| Sensitivity | Tenderness and discomfort, particularly when eating or drinking |
Duration and Persistence
The duration and persistence of swollen gums can vary depending on the underlying cause. Swollen gums can be a temporary condition resulting from factors such as dental issues, infections, hormonal changes, or vitamin deficiencies. However, if the swelling persists for an extended period, it may indicate a more serious condition like periodontal disease, which can lead to the destruction of the underlying jawbone and potential tooth loss if left untreated.
| Condition | Duration |
|---|---|
| Temporary Swelling | Caused by infections, hormonal changes, or vitamin deficiencies |
| Persistent Swelling | May indicate gum disease or other serious conditions |
Understanding the symptoms and characteristics of swollen gums is crucial for identifying the underlying causes and seeking appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Swollen Gums
Addressing the causes of swollen gums is essential for maintaining oral health. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here, we explore dental treatments, medications, and lifestyle changes that can help alleviate swollen gums.
Dental Treatments
Dental treatments are often necessary to address the root causes of swollen gums. Common procedures include:
- Deep Cleaning: Also known as scaling and root planing, this procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line, helping to reduce inflammation and prevent gum disease progression.
- Root Canal Therapy: If an infection has spread to the tooth pulp, a root canal may be required to remove the infected tissue and save the tooth.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary to prevent further infection and damage to surrounding teeth.
| Treatment Type | Purpose | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Cleaning | Remove plaque and tartar | 1-2 hours |
| Root Canal Therapy | Remove infected tooth pulp | 1-2 visits |
| Tooth Extraction | Remove severely damaged or infected tooth | 30-60 minutes |
If swollen gums persist for more than two weeks, it is advisable to seek professional dental care. Prompt treatment can prevent issues from worsening and alleviate severe pain.
Medications
Medications can also play a role in treating swollen gums. These may include:
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to treat bacterial infections causing gum inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Help reduce swelling and pain in the gums.
- Antiseptic Mouthwash: Used to control plaque and reduce gum inflammation.
| Medication Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Treat bacterial infections | Amoxicillin |
| Anti-inflammatory Drugs | Reduce swelling and pain | Ibuprofen |
| Antiseptic Mouthwash | Control plaque and reduce inflammation | Chlorhexidine |
Severe pain that does not improve with medication should prompt immediate dental care.
Lifestyle Changes
Incorporating healthy habits into daily routines can significantly impact the health of your gums. Key lifestyle changes include:
- Oral Hygiene Practices: Brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can help prevent and reverse gingivitis.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visiting the dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups can help detect and treat gum issues early.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall oral health.
- Avoiding Tobacco: Smoking and using tobacco products can exacerbate gum problems and hinder healing.
By understanding and addressing the causes of swollen gums, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their oral health. Whether through professional dental treatments, medications, or lifestyle changes, managing swollen gums is essential for preventing further complications and ensuring a healthy smile.
Preventive Measures for Swollen Gums
Preventing swollen gums involves a combination of good oral hygiene practices, regular dental checkups, and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits. These measures can help reduce the risk of gum disease and other oral health issues.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for preventing swollen gums. Key practices include:
- Brushing: Brush teeth at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste. This helps remove plaque and food particles that can cause gum inflammation.
- Flossing: Floss daily to remove plaque and debris from between the teeth and under the gumline, areas that a toothbrush cannot reach.
- Mouthwash: Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and freshen breath.
These practices can help prevent and reverse gingivitis, a common cause of swollen gums.
Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental visits are crucial for maintaining oral health and preventing swollen gums. During these checkups, a dentist can:
- Professional Cleaning: Remove tartar and plaque buildup that cannot be eliminated by regular brushing and flossing.
- Examination: Identify early signs of gum disease and other oral health issues.
- Advice: Provide personalized recommendations for improving oral hygiene practices.
Early detection and treatment of gum disease can help manage oral health more effectively.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can also play a significant role in preventing swollen gums. These habits include:
- Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, which are essential for healthy gums.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep the mouth hydrated and wash away food particles and bacteria.
- Avoid Tobacco: Refrain from smoking or using other tobacco products, as they can contribute to gum disease and other oral health issues.
- Manage Stress: Reduce stress through relaxation techniques, as stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of gum inflammation.
By incorporating these preventive measures into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of swollen gums and maintain better overall oral health.
SOURCES:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24907-swollen-gums
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/in-depth/dental/art-20047475
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/248423
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gingivitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354453
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21482-gum-periodontal-disease
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/facial-swelling
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/swelling
https://www.healthline.com/health/skin-lumps
Need Assistance? We’re Here to Help
We are dedicated to enhancing your dental health and well-being.
We provide personalized dental care solutions for a confident, healthy smile.
Contact us today for Professional Dental Care.

Our caring staff will help you feel relaxed and comfortable in our state of the art office. We respect your time and pledge to deliver prompt service, backed by the latest knowledge, techniques, and technology.
Email: Office@schwimmerdental.com
Tel: (848) 294-2385
Fax: (732) 899-3347
Address: 1115 Arnold Ave,
Point Pleasant, NJ, 08742
Schwimmer Dental – Website by CWS