Have an appointment? Complete the Intake Form
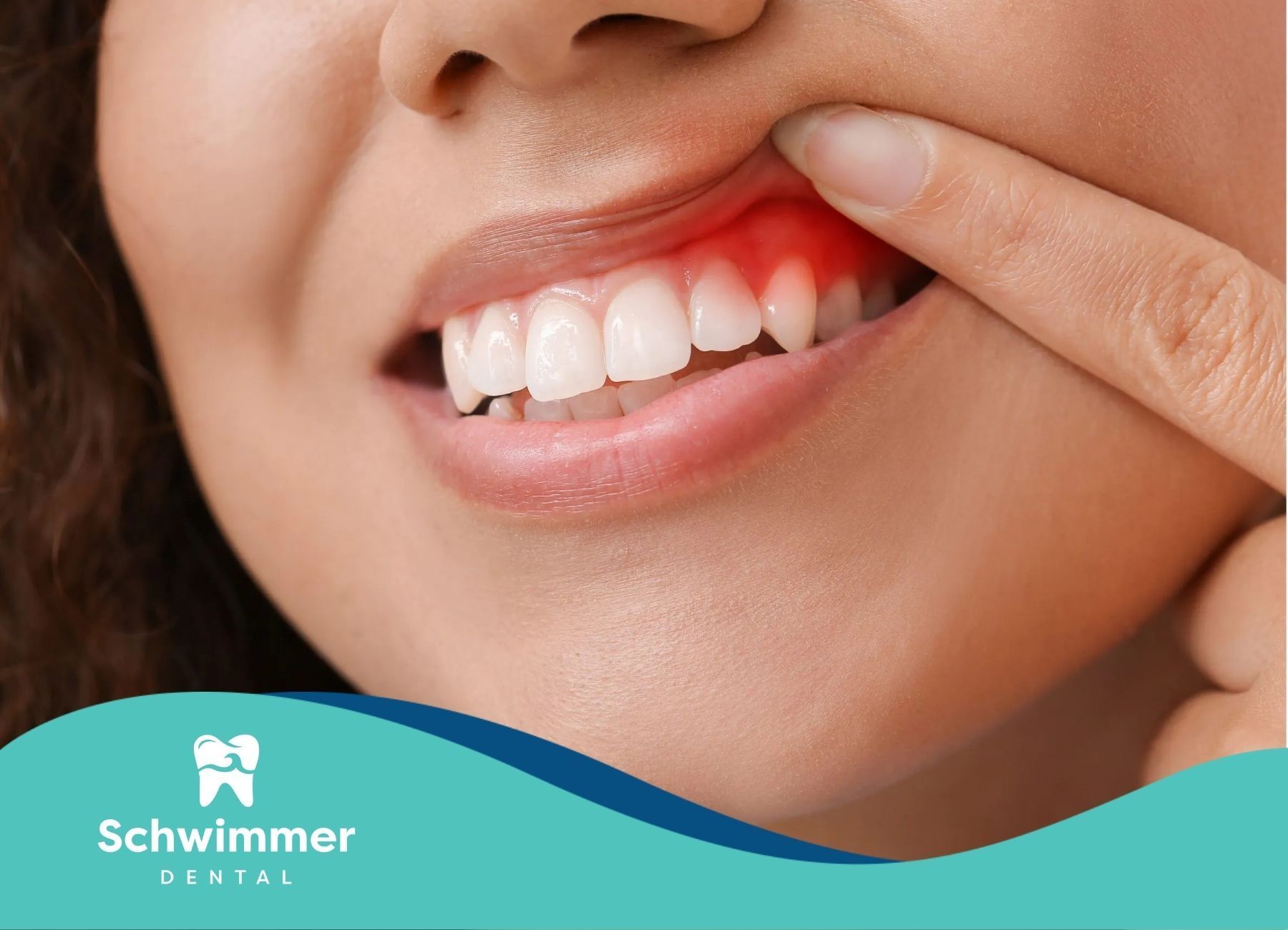
Understanding Common Causes of Swollen Gums Around Tooth
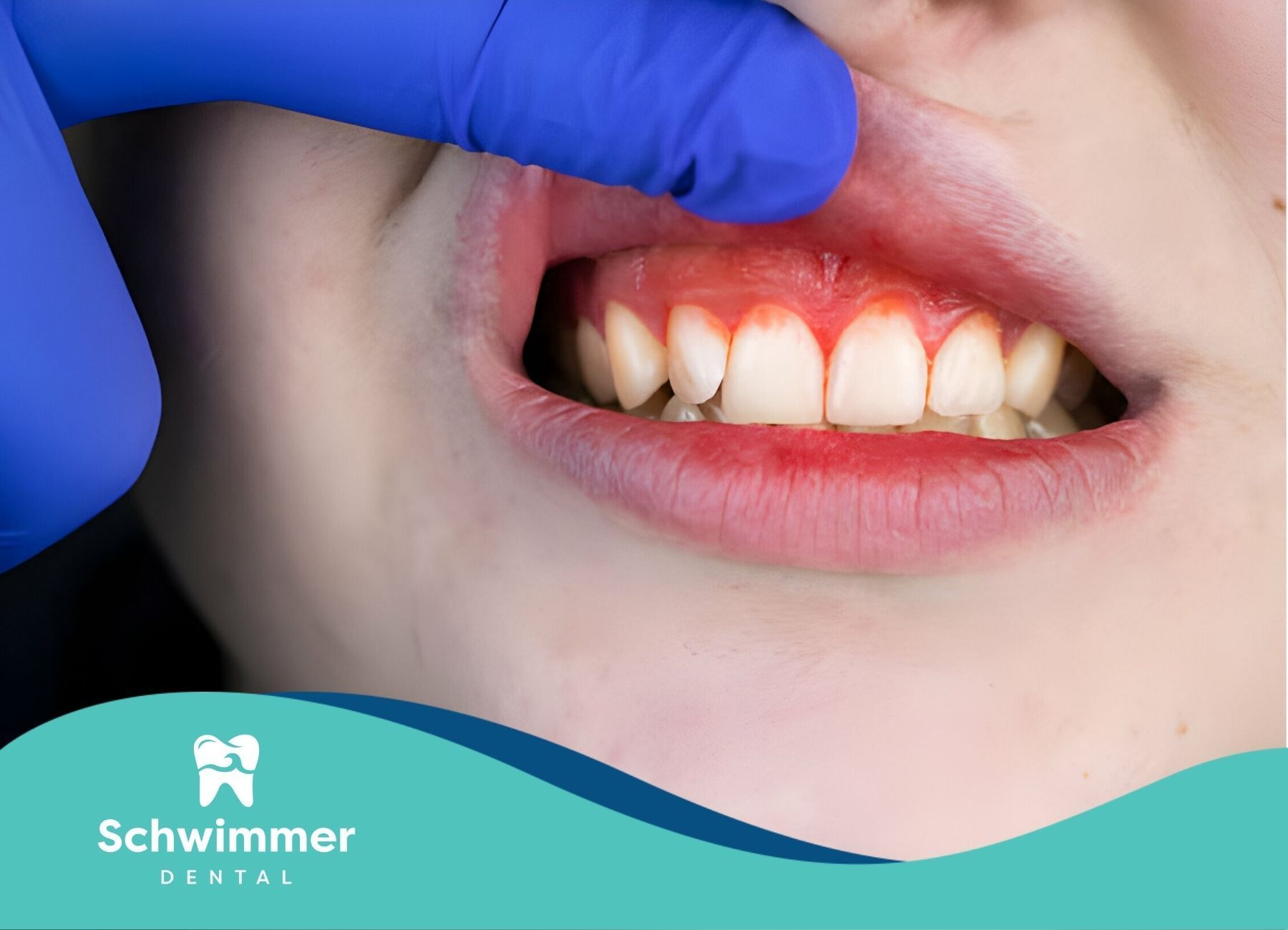
Causes of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums often occur due to bacterial infection or irritation of the gum tissue. However, there are several other potential causes:
- Gingivitis: This is the most common cause of swollen gums. Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease characterized by inflammation of the gums due to plaque buildup.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Deficiencies in essential vitamins, particularly vitamins B and C, can lead to gum swelling. For instance, low levels of vitamin C can cause scurvy, which results in anemia and gum disease.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during pregnancy, can increase blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to irritation and swelling.
- Infections:
Fungal and viral infections, such as herpes or thrush, can cause swollen gums. Additionally, untreated dental decay can lead to a dental abscess, resulting in localized gum swelling that requires professional treatment.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications can cause gum swelling as a side effect. These may include drugs for blood pressure, immunosuppressants, and some anticonvulsants.
Common Triggers for Gum Swelling
Several common triggers can exacerbate gum swelling, making it important to identify and manage these factors:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which irritates the gums and causes swelling. For more information on the impact of poor oral hygiene, visit our section on swollen gums and oral health.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using other tobacco products can irritate the gums and contribute to inflammation and swelling.
- Stress: High levels of stress can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections that cause gum swelling.
- Diet: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can lead to deficiencies that contribute to gum swelling. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is crucial for maintaining healthy gums.
- Dental Appliances: Ill-fitting dentures, braces, or other dental appliances can irritate the gums and cause swelling.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Inflammation due to plaque buildup |
| Nutrient Deficiencies | Lack of vitamins B and C |
| Hormonal Changes | Increased blood flow during pregnancy |
| Infections | Fungal and viral infections like herpes or thrush |
| Medication Side Effects | Drugs for blood pressure, immunosuppressants, anticonvulsants |
Understanding the causes and common triggers of swollen gums is essential for effective management and prevention. For more detailed information on the reasons for swollen gums, visit our article on reasons for swollen gums. Additionally, explore our section on swollen gums home remedies for tips on alleviating gum inflammation at home.
Factors Contributing to Swollen Gums
Swollen gums around a tooth can be caused by various factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Bacterial Infections and Gum Swelling
Bacterial infections are a primary cause of swollen gums. Gingivitis, the most common form of gum disease, typically occurs due to bacterial infection of the gum tissue. Without proper dental hygiene, plaque can build up around the tooth base, leading to infection and inflammation.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup. |
| Periodontitis | Advanced gum disease that can damage the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. |
Bacterial infections can lead to symptoms such as redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. For more information on the symptoms and treatment of gum disease, visit our article on swollen gums and bleeding.
Other Potential Causes of Gum Swelling
While bacterial infections are a common cause, other factors can also contribute to swollen gums. These include:
- Malnutrition: Deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals can lead to gum swelling. For instance, a lack of vitamin C can cause scurvy, which manifests as swollen and bleeding gums.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can cause hormonal fluctuations that increase blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to swelling.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications, such as anticonvulsants and immunosuppressants, can cause gum overgrowth and swelling.
- Food Particles: Simple causes like getting food particles stuck in the teeth can lead to gum irritation. For example, popcorn kernels can become lodged in the gums, causing inflammation.
For more detailed information on the various causes of swollen gums, visit our page on swollen gums causes. Understanding the different factors that contribute to swollen gums can help in identifying the underlying cause and seeking appropriate treatment.
Swollen Gums and Oral Health
Impact of Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene is a significant contributor to swollen gums around the tooth. When dental hygiene practices are neglected, plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—accumulates on the teeth and gum line. This buildup can lead to gingivitis, the most common form of gum disease. Gingivitis is characterized by inflammation, redness, and swelling of the gums.
Without proper dental care, plaque hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. The presence of tartar exacerbates gum irritation and can lead to more severe forms of gum disease, such as periodontitis. Periodontitis can cause significant damage to the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss.
| Oral Hygiene Practice | Impact on Gum Health |
|---|---|
| Brushing twice daily | Reduces plaque buildup |
| Flossing daily | Removes plaque between teeth |
| Regular dental check-ups | Early detection and removal of tartar |
| Using mouthwash | Reduces bacteria in the mouth |
Hormonal Changes and Gum Swelling
Hormonal changes can also play a significant role in the development of swollen gums. These changes can alter the environment in the mouth, making it more susceptible to infections and inflammation. This is particularly evident during pregnancy, puberty, menstruation, and menopause.
During pregnancy, increased levels of progesterone can enhance the blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to swelling. This condition, known as pregnancy gingivitis, affects many pregnant women and can be managed with good oral hygiene practices and regular dental visits.
| Hormonal Stage | Impact on Gums |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy | Increased sensitivity and swelling |
| Puberty | Heightened response to plaque |
| Menstruation | Temporary gum inflammation |
| Menopause | Dry mouth and gum recession |
Understanding the link between hormonal changes and gum health is crucial for managing and preventing gum swelling.
By maintaining good oral hygiene and being aware of the factors that contribute to swollen gums, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure their gum health. Regular dental check-ups and proper care are essential in preventing and managing gum-related issues.
Remedies for Swollen Gums
Swollen gums around a tooth can be uncomfortable and concerning. Addressing this issue involves both home remedies and medical treatments. Here, we explore effective solutions for managing gum inflammation.
Home Remedies for Gum Inflammation
Home remedies can provide relief and promote healing for swollen gums. These methods are often easy to implement and can be done with items commonly found at home.
- Saltwater Rinse: A saltwater rinse can soothe gum inflammation and promote healing. Mix 1 teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and rinse your mouth thoroughly. This can be done several times a day.
- Turmeric Gel: Turmeric contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties. Applying turmeric gel to the gums may help prevent plaque and gingivitis, common causes of swollen gums.
- Aloe Vera Mouthwash: Aloe vera is known for its healing properties. Using an aloe vera mouthwash can be as effective as chlorhexidine in curing and preventing gingivitis.
- Antiseptic Mouthwash: Using an antiseptic mouthwash can help control plaque buildup and reduce inflammation.
- Tea Tree Oil Rinse: Tea tree oil has antimicrobial properties. Adding a few drops to water and using it as a mouth rinse can help reduce gum inflammation.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Medical Treatments for Gum Swelling
When home remedies are not sufficient, medical treatments may be necessary to address the underlying causes of swollen gums. These treatments are typically performed by dental professionals.
- Tooth Scaling and Polishing: This procedure removes tartar and plaque from the teeth and below the gumline, helping to reduce inflammation.
- Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure smooths the roots of the teeth, making it harder for bacteria to attach and grow.
- Antibiotics: In cases of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Incision and Drainage: If an abscess is present, it may need to be drained to relieve pressure and remove pus.
- Root Canal: This procedure removes bacteria from infected tooth roots, preventing further infection and inflammation.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases, removing the affected tooth may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection.
By combining home remedies with professional medical treatments, individuals can effectively manage and reduce gum inflammation. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential for maintaining healthy gums and preventing future issues.
Preventive Measures for Gum Health
Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for maintaining healthy gums and preventing issues such as swollen gums around a tooth. It is recommended that individuals have a dental check-up at least once or twice a year, even if they do not have any symptoms. These visits allow for early detection and treatment of any dental problems, which can prevent complications and ensure overall oral health.
During a dental check-up, the dentist will examine the gums for signs of inflammation, bleeding, or tenderness. If any issues are detected, the dentist may recommend a more thorough cleaning or refer the patient to a periodontist for specialized treatment. Regular dental visits, combined with good oral hygiene practices, are essential for preventing gum disease and maintaining healthy gums.
Oral Hygiene Practices for Healthy Gums
Practicing good oral hygiene is key to preventing swollen gums and maintaining overall oral health. Here are some essential oral hygiene practices:
- Brushing: Brush teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle to the gums and use gentle, circular motions to clean all surfaces of the teeth.
- Flossing: Clean between teeth daily with dental floss or an interdental cleaner to remove plaque and food particles that a toothbrush cannot reach.
- Mouthrinse: Use an antimicrobial mouthrinse to help reduce plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Diet: Maintain a balanced diet and limit sugary snacks and drinks, which can contribute to plaque buildup and gum inflammation.
| Oral Hygiene Practice | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Brushing | Twice daily |
| Flossing | Once daily |
| Mouthrinse | Once daily |
| Dental Check-up | Once or twice a year |
Following these practices can help prevent swollen gums and other oral health issues. If swollen gums persist or cause concern, it is important to seek immediate attention from a dental professional.
Swollen Gums and Periodontal Disease
Symptoms of Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a severe gum infection that can lead to significant oral health issues if left untreated. It is one of the primary causes of swollen gums around a tooth. Recognizing the symptoms early can help prevent further complications. Common symptoms of periodontitis include:
- Sore, swollen gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth
- Painful chewing
These symptoms indicate the presence of an infection that can lead to tooth loss, bone loss, and other oral health problems. It's crucial to address these symptoms promptly to avoid more severe consequences.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
Treating periodontitis involves a combination of professional dental care and at-home oral hygiene practices. The treatment approach depends on the severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment options:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep-cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line. It also smooths the tooth roots to help gums reattach to the teeth.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection.
Surgical Treatments
- Flap Surgery: This procedure involves lifting the gums to remove tartar deposits in deep pockets. The gums are then sutured back in place to fit snugly around the teeth.
- Bone Grafts: Used to replace bone destroyed by periodontitis, bone grafts promote the regrowth of bone in the affected areas.
- Soft Tissue Grafts: This procedure reinforces thin gums or fills in areas where gums have receded.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: This technique stimulates the growth of bone and gum tissue.
| Treatment Type | Description | Severity Addressed |
|---|---|---|
| Scaling and Root Planing | Deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar | Mild to Moderate |
| Antibiotics | Control bacterial infection | Mild to Moderate |
| Flap Surgery | Remove tartar deposits in deep pockets | Severe |
| Bone Grafts | Replace destroyed bone | Severe |
| Soft Tissue Grafts | Reinforce or fill in receded gums | Severe |
| Guided Tissue Regeneration | Stimulate growth of bone and gum tissue | Severe |
Early intervention is key to managing periodontitis effectively. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene can prevent the progression of the disease. For those experiencing symptoms of periodontitis, seeking prompt treatment can prevent the need for more extensive and costly procedures.
SOURCES:
https://www.healthline.com/health/gums-swollen
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/swollen-gums
https://www.healthline.com/health/home-remedies-for-swollen-gums
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24907-swollen-gums
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326016
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16620-periodontitis
Need Assistance? We’re Here to Help
We are dedicated to enhancing your dental health and well-being.
We provide personalized dental care solutions for a confident, healthy smile.
Contact us today for Professional Dental Care.

Our caring staff will help you feel relaxed and comfortable in our state of the art office. We respect your time and pledge to deliver prompt service, backed by the latest knowledge, techniques, and technology.
Email: Office@schwimmerdental.com
Tel: (848) 294-2385
Fax: (732) 899-3347
Address: 1115 Arnold Ave,
Point Pleasant, NJ, 08742
Schwimmer Dental – Website by CWS