Have an appointment? Complete the Intake Form
A Helpful Guide to Identifying Swollen Gums and Bleeding
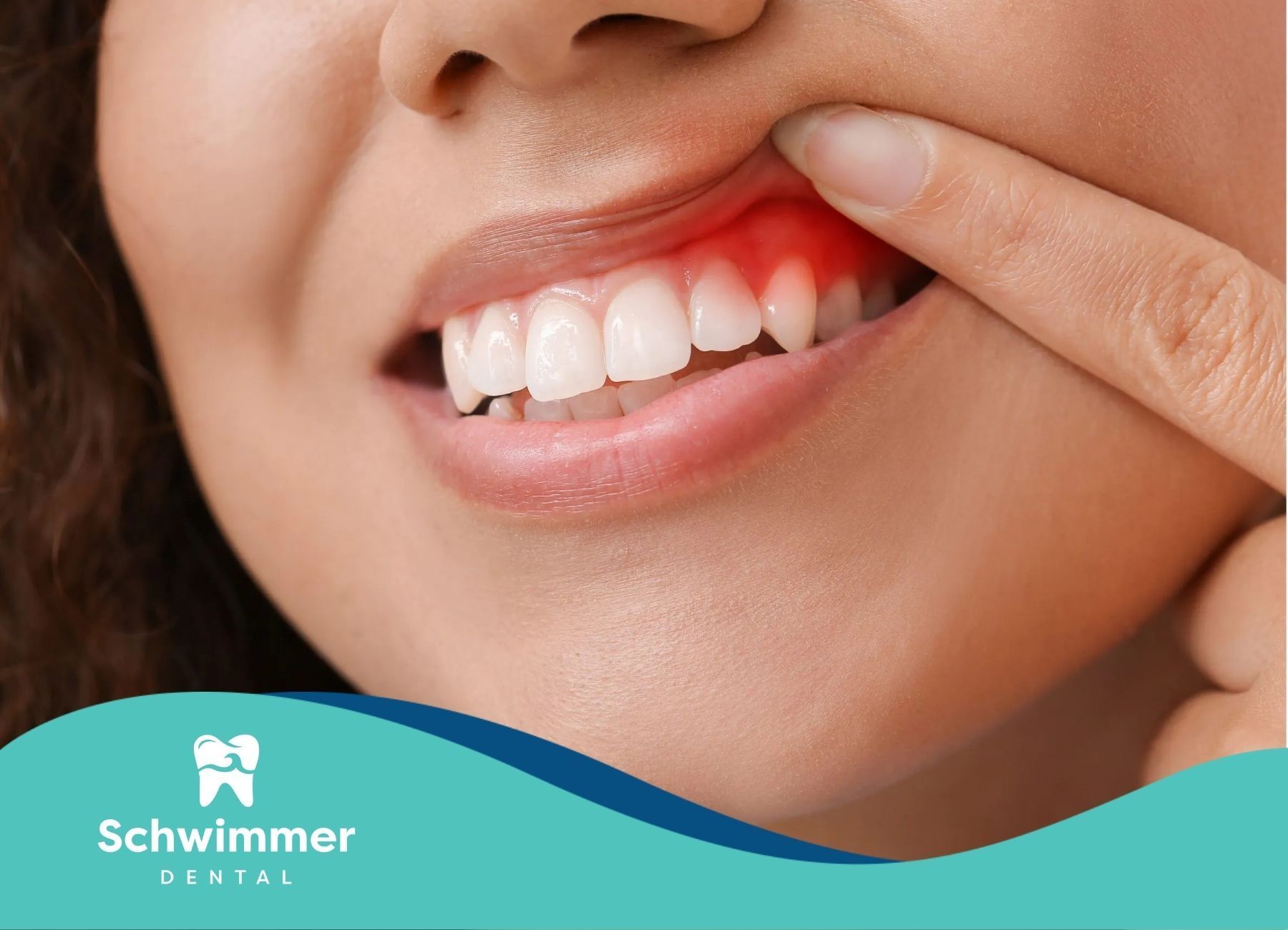
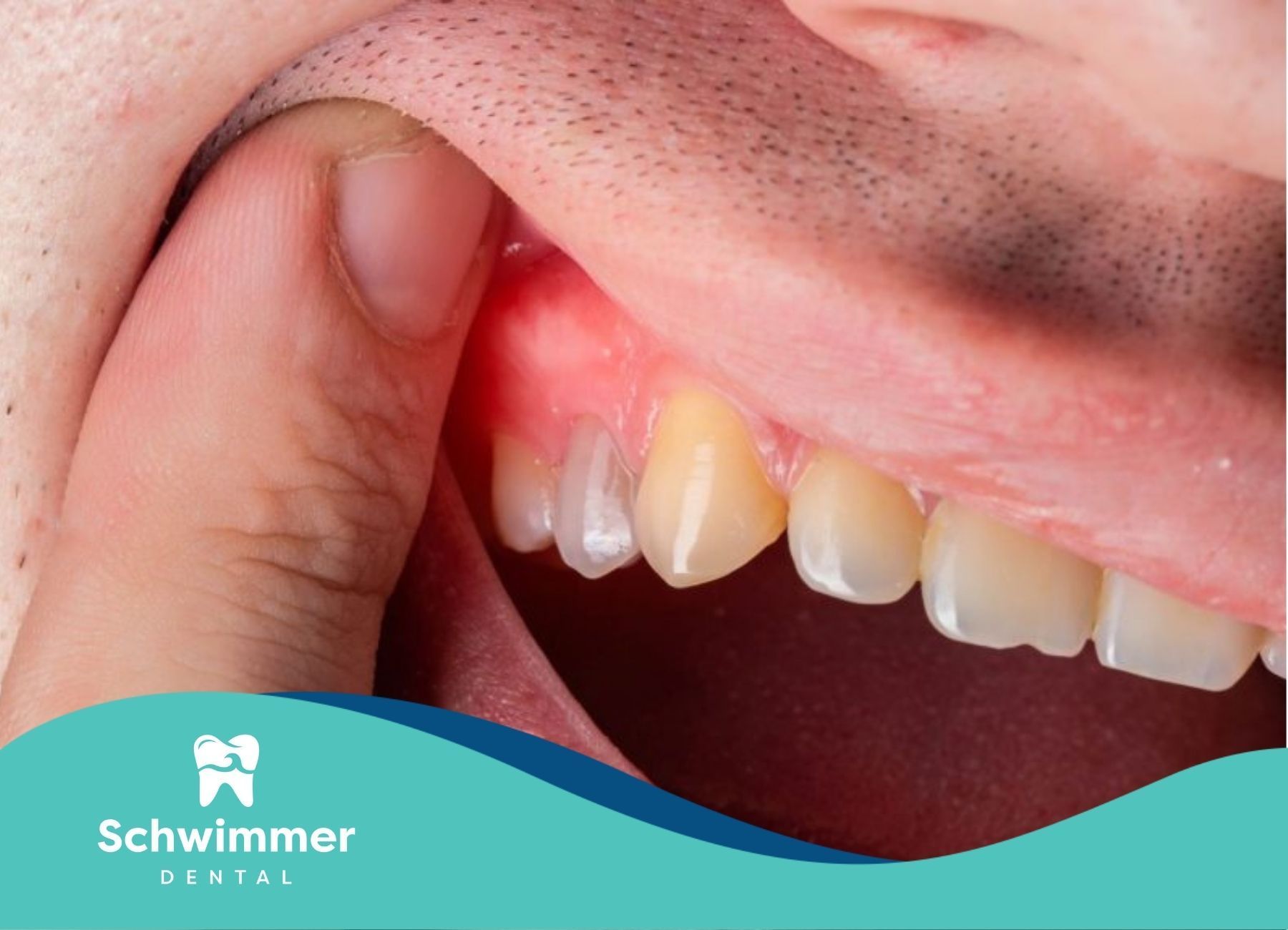
Understanding Swollen Gums
Swollen gums are a common oral health issue that can affect individuals of all ages. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of swollen gums is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
Symptoms of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums are often characterized by several noticeable symptoms. These symptoms can help identify the condition early and seek appropriate treatment.
- Redness or Purplish Hue: Swollen gums usually have a reddish or purplish color due to increased blood flow.
- Smooth or Shiny Appearance: The gums may appear smooth or shiny, indicating inflammation.
- Bleeding: Swollen gums often bleed, especially during brushing or flossing.
- Tenderness or Pain: The gums may feel tender or painful to the touch.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath can accompany swollen gums.
Causes of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums can result from various factors, ranging from dental issues to underlying health conditions. Understanding these causes can help in identifying the appropriate treatment.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Gingivitis | A common form of gum disease caused by plaque buildup on the teeth. |
| Infections | Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to gum swelling. |
| Vitamin Deficiencies | Lack of essential vitamins, such as vitamin C, can cause swollen gums. |
| Hormonal Changes | Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can affect gum health. |
| Diabetes | Individuals with diabetes are more prone to gum infections and swelling. |
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup and gum inflammation. |
For more detailed information on the causes of swollen gums, visit our page on swollen gums causes.
Swollen gums can be a temporary or permanent condition, depending on the underlying cause. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications and maintain good oral health. If you experience persistent gum swelling, it is advisable to seek professional dental care. For home remedies and additional tips, check out our article on swollen gums home remedies.
Gum Disease: Gingivitis
Overview of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an early form of gum disease that occurs when plaque builds up on teeth along the gum line, leading to irritation, bleeding, and swelling of the gums. This condition is quite common, with almost half of all adults older than 30 experiencing some form of gum disease. In Australia, about 1 in 5 individuals has gingivitis.
The primary cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to accumulate on the teeth. This plaque can harden into tartar, further irritating the gums and causing inflammation. Symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Red, swollen gums
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Bad breath
- Receding gums
Gingivitis is reversible with proper care and maintenance. Regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day and flossing daily, can help prevent and treat gingivitis.
Progression to Periodontitis
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe type of gum disease involving bone loss in the jaw. Periodontitis not only affects the gums but also the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone. This can lead to tooth mobility and eventual tooth loss.
The progression from gingivitis to periodontitis involves the following stages:
- Gingivitis: Inflammation of the gums without affecting the bone.
- Early Periodontitis: The gums begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. The bone starts to break down.
- Moderate Periodontitis: The infection spreads, leading to further bone loss and deeper pockets.
- Advanced Periodontitis: Significant bone loss occurs, teeth may become loose, and there is a high risk of tooth loss.
| Stage | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Red, swollen gums, bleeding | Professional cleaning, improved oral hygiene |
| Early Periodontitis | Gums pulling away, pockets forming | Scaling and root planing, improved oral hygiene |
| Moderate Periodontitis | Deeper pockets, more bone loss | Scaling and root planing, possible surgical intervention |
| Advanced Periodontitis | Significant bone loss, loose teeth | Surgical intervention, possible tooth extraction |
Early intervention is crucial to prevent the progression of gingivitis to periodontitis. Regular dental visits and maintaining good oral hygiene can help manage and prevent gum disease.
Understanding the importance of early treatment and preventive measures can help maintain healthy gums and prevent the complications associated with gum disease. For more information on the reasons behind swollen gums, check out our article on reasons for swollen gums.
Periodontitis: Severe Gum Disease
Periodontitis is a severe form of gum disease that can have significant impacts on oral health. Understanding its effects and the risk factors associated with it is crucial for prevention and management.
Impact of Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an oral health condition that causes sore, bleeding, and swollen gums. If left untreated, it can lead to several serious complications, including:
- Tooth Loss: The infection can destroy the bone that supports the teeth, leading to tooth loss.
- Bone Loss: The disease can cause the jawbone to deteriorate, affecting the structure and function of the mouth.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath is a common symptom due to the presence of bacteria and infection.
- Other Oral Health Problems: Periodontitis can lead to abscesses, receding gums, and increased sensitivity.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, almost half of all adults in the United States have some form of gum disease, making it the leading cause of tooth loss.
Risk Factors for Periodontitis
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing periodontitis. These include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow bacteria to create plaque and tartar, leading to infection.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor and can hinder treatment effectiveness.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can contribute to gum disease.
- Certain Medications: Some drugs can reduce saliva flow, affecting oral health.
- Genetics: Family history can make some individuals more prone to periodontitis.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions that compromise the immune system can increase susceptibility.
Risk Factors and Their Impact on Periodontitis
Periodontitis is more likely to occur as individuals age and is most common in people over 30. However, it can affect anyone with poor oral hygiene.
If you are experiencing symptoms, early intervention is crucial. Explore our swollen gums home remedies for initial relief and consult a dental professional for comprehensive care.
Seeking Treatment for Swollen Gums
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is crucial when dealing with swollen gums and bleeding. If you develop sore, swollen, or bleeding gums, it is advised to schedule an appointment with a dentist right away. Prompt treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and help restore oral health. Swollen gums can be a temporary or permanent condition and can result from dental issues or underlying health conditions like infections, diabetes, or vitamin deficiencies.
Treatment Options for Swollen Gums
The treatment for swollen gums depends on the underlying cause. For gum disease, a dentist or periodontist can recommend appropriate treatments. Common dental treatments for swollen gums include:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line, helping to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Antibiotics: In cases of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate bacteria and reduce swelling.
- Surgery: For severe cases, surgical interventions such as flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts may be necessary to restore gum health.
Swollen gums can go away with proper treatment, but if caused by gum disease, treatment is necessary. Prompt treatment is advised if gum swelling lasts longer than a couple of weeks to prevent issues from worsening.
Preventive Measures for Gum Health
Maintaining healthy gums is crucial for overall oral health. Preventive measures can help avoid issues such as swollen gums and bleeding. This section will cover essential practices for maintaining good oral hygiene and lifestyle factors that affect gum health.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
Proper oral hygiene is the cornerstone of preventing gum disease and maintaining healthy gums. Here are key practices to follow:
- Brushing:
Brush teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. This helps remove plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that can cause gingivitis if not removed.
- Flossing: Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and under the gumline. This prevents the buildup of plaque in areas that a toothbrush cannot reach.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visit the dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups. Professional cleanings remove tartar, which cannot be removed by brushing and flossing alone.
- Mouthwash: Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria in the mouth and help prevent gum disease.
| Oral Hygiene Practice | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Brushing | Twice daily |
| Flossing | Daily |
| Dental Checkups | Every 6 months |
| Mouthwash | As recommended |
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Gum Health
In addition to maintaining good oral hygiene, certain lifestyle factors can significantly impact gum health. Here are some important considerations:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports gum health. Foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and leafy greens, help strengthen gums and prevent inflammation.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, reducing the risk of plaque buildup.
- Smoking: Avoid smoking and using tobacco products. Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease and can exacerbate symptoms of swollen gums and bleeding.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
By incorporating these preventive measures into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease and maintain healthy gums.
Additional Causes of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums are a common symptom of gingivitis and other types of gum disease, but they can also indicate other health conditions. Understanding these additional causes can help in identifying the root of the problem and seeking appropriate treatment.
Other Health Conditions
Swollen gums can be a sign of various underlying health conditions. These conditions may not be directly related to oral health but can still impact the gums significantly.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to gum swelling. Conditions like herpes simplex virus or oral thrush can cause inflammation and discomfort in the gums.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins, particularly Vitamin C (scurvy) and Vitamin B, can result in swollen gums. These deficiencies weaken the immune system and affect the body's ability to maintain healthy gum tissue.
- Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can cause gums to swell. These changes increase blood flow to the gum tissue, making it more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to infections, including those affecting the gums. High blood sugar levels can impair the body's ability to fight off infections, leading to swollen and bleeding gums.
Uncommon Factors Leading to Gum Swelling
While less common, certain factors can also contribute to swollen gums. These factors may not be immediately obvious but can still have a significant impact on gum health.
- Medication Side Effects: Some medications, such as antihypertensives, immunosuppressants, and certain anticonvulsants, can cause gum swelling as a side effect. These medications can lead to an overgrowth of gum tissue, resulting in inflammation and discomfort.
- Malnutrition: Poor nutrition can weaken the immune system and affect overall health, including the gums. A diet lacking in essential nutrients can lead to gum inflammation and increase the risk of infections.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies to certain foods, dental products, or materials used in dental procedures can cause gum swelling. Identifying and avoiding the allergen can help alleviate the symptoms.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using other tobacco products can irritate the gum tissue and lead to inflammation. Tobacco use also impairs the body's ability to heal, making it harder to treat gum swelling effectively.
| Health Condition | Impact on Gums |
|---|---|
| Infections | Causes inflammation and discomfort |
| Vitamin Deficiencies | Weakens immune system, affects gum health |
| Hormonal Changes | Increases blood flow, sensitivity |
| Diabetes | Impairs infection-fighting ability |
| Medication Side Effects | Leads to gum overgrowth |
| Malnutrition | Weakens immune system, increases infection risk |
| Allergic Reactions | Causes inflammation |
| Tobacco Use | Irritates gum tissue, impairs healing |
Understanding these additional causes of swollen gums can help in identifying the root of the problem and seeking appropriate treatment.
SOURCES:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16620-periodontitis
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24907-swollen-gums
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/gingivitis
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10950-gingivitis-and-periodontal-disease-gum-disease
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/swollen-gums
Need Assistance? We’re Here to Help
We are dedicated to enhancing your dental health and well-being.
We provide personalized dental care solutions for a confident, healthy smile.
Contact us today for Professional Dental Care.

Our caring staff will help you feel relaxed and comfortable in our state of the art office. We respect your time and pledge to deliver prompt service, backed by the latest knowledge, techniques, and technology.
Email: Office@schwimmerdental.com
Tel: (848) 294-2385
Fax: (732) 899-3347
Address: 1115 Arnold Ave,
Point Pleasant, NJ, 08742
Schwimmer Dental – Website by CWS