Have an appointment? Complete the Intake Form
Understanding the Top Reasons for Swollen Gums Today
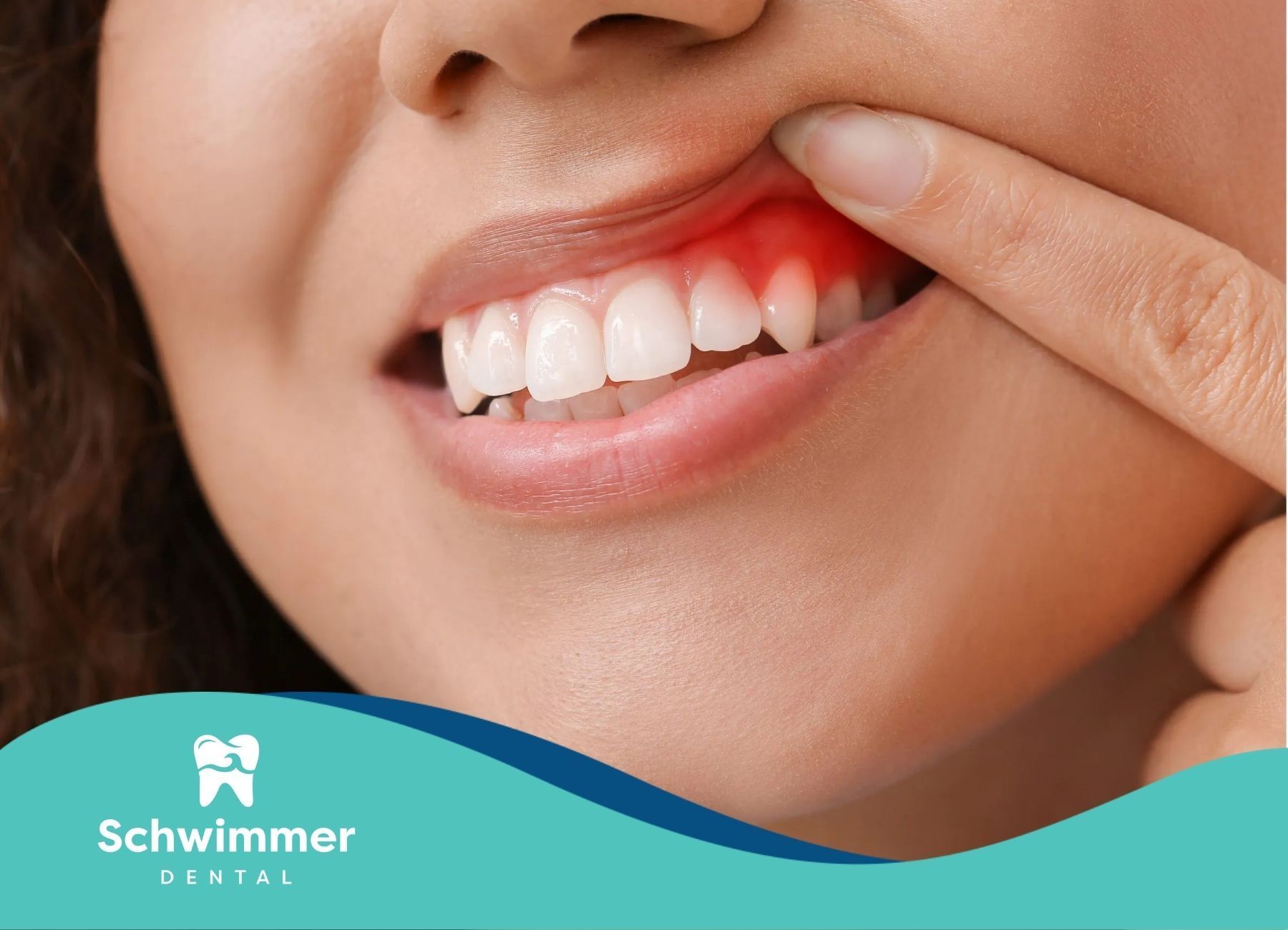
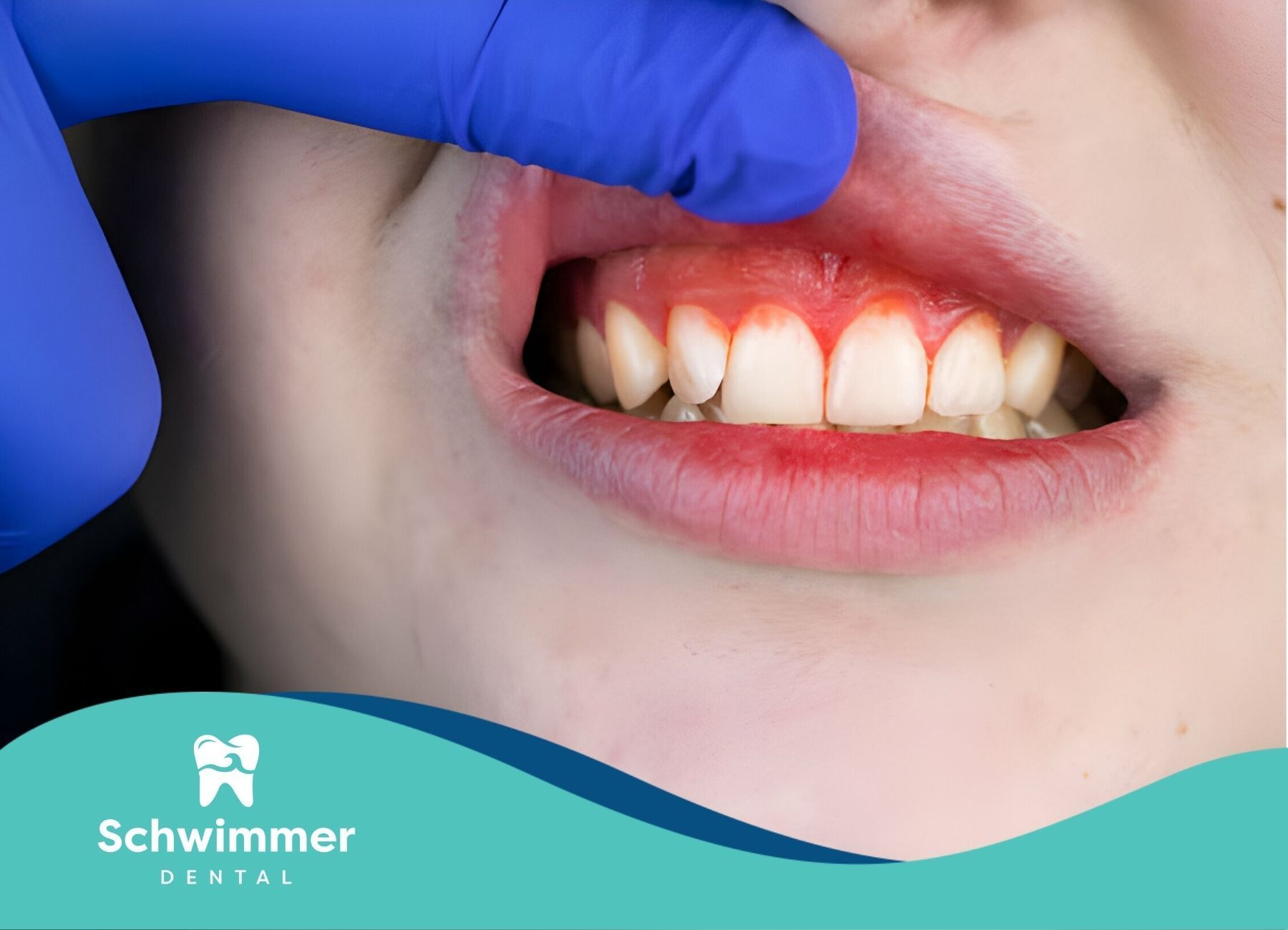
Understanding Swollen Gums
Swollen gums are a common oral health issue that can affect individuals of all ages. Understanding the definition, characteristics, and common symptoms of swollen gums is essential for identifying and addressing this condition effectively.
Definition and Characteristics
Swollen gums, also known as gingival swelling, refer to the enlargement or inflammation of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth. This condition can be temporary or chronic, depending on the underlying cause. Swollen gums are often a symptom of gingivitis and other types of gum disease, but they can also indicate other health conditions such as infections, vitamin deficiencies, or hormonal changes.
Characteristics of swollen gums include:
- A reddish or purplish hue due to increased blood flow
- A smooth or shiny appearance
- Bleeding, especially when brushing or flossing
Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of swollen gums is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms associated with swollen gums include:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Redness | Gums appear red or purplish due to increased blood flow |
| Swelling | Gums are enlarged and may feel puffy or tender |
| Bleeding | Gums bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing |
| Pain | Gums may be sore or painful to the touch |
| Bad Breath | Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth |
Swollen gums can result from various factors, including dental issues, infections, hormonal changes, vitamin deficiencies, or underlying health conditions. For more information on the causes of swollen gums, visit our article on swollen gums causes.
Understanding the symptoms and characteristics of swollen gums can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and maintain their oral health. For tips on managing swollen gums at home, check out our guide on swollen gums home remedies.
Causes of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums can be a sign of various underlying issues. Understanding the reasons for swollen gums is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Here are some common causes:
Gum Disease and Gingivitis
Gum disease, particularly gingivitis, is a leading cause of swollen gums. Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup on the teeth. Poor oral hygiene, such as not brushing or flossing regularly, allows plaque to form, leading to swollen, tender gums that may bleed easily.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Swelling | Gums appear puffy and enlarged |
| Redness | Gums are bright or dark red |
| Tenderness | Gums are sensitive to touch |
| Bleeding | Gums bleed easily, especially when brushing |
For more information on managing gingivitis, visit our page on swollen gums and bleeding.
Infections and Health Conditions
Infections and other health conditions can also cause swollen gums. Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to gum inflammation. Conditions such as herpes simplex virus, thrush, and even systemic diseases like diabetes can contribute to gum swelling.
| Infection/Condition | Impact on Gums |
|---|---|
| Herpes Simplex Virus | Causes painful sores and swollen gums |
| Thrush (Oral Candidiasis) | Leads to white patches and gum swelling |
| Diabetes | Increases risk of infections and gum disease |
Hormonal Changes and Vitamin Deficiencies
Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, can cause gums to swell. These changes increase blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to swelling. Additionally, vitamin deficiencies, especially vitamin C deficiency (scurvy), can lead to swollen gums.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy | Hormonal fluctuations increase gum sensitivity |
| Menstruation | Hormonal changes can cause temporary gum swelling |
| Vitamin C Deficiency | Leads to weakened gum tissue and swelling |
Maintaining good oral hygiene and a balanced diet can help prevent these issues.
Understanding these causes can help in identifying the appropriate treatment and preventive measures. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential in managing and preventing swollen gums.
Impact of Swollen Gums
Swollen gums can have significant implications for both oral and overall health. Understanding these impacts is crucial for individuals experiencing this condition and for those providing care.
Oral Health Consequences
Swollen gums are often a symptom of underlying oral health issues such as gingivitis and other types of gum disease. If left untreated, these conditions can progress and lead to more severe complications.
| Condition | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Inflammation and bleeding of gums |
| Periodontitis | Damage to gum tissue and bone, potential tooth loss |
| Tooth Decay | Increased risk due to poor oral hygiene |
Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, a severe gum disease that affects the tissues and bones supporting the teeth. This can result in tooth loss and other serious dental issues. For more information on the progression of gum disease, visit our article on swollen gums around tooth.
Link to Overall Health
The health of the gums is closely linked to overall health. The mouth serves as the entry point to the digestive and respiratory tracts, making it a critical area for maintaining overall health. Germs and inflammation in the mouth can contribute to various systemic conditions.
| Health Condition | Link to Oral Health |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | Difficulty controlling blood sugar levels, exacerbated by gum disease |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Potential link between gum disease and heart conditions |
| Respiratory Infections | Germs from the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs |
New Paragraph
| Condition | Characteristics | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Inflammation of the gums, mild swelling, redness | Reversible with treatment |
| Periodontitis | Damage to tissue and bone, gum recession, tooth loss | Irreversible, but manageable |
Early detection and treatment of gingivitis are essential to prevent the progression to periodontitis. Regular dental cleanings and diligent oral hygiene can reverse gingivitis, but once periodontitis sets in, the damage cannot be fully undone.
Potential Tooth Loss and Health Risks
Periodontitis can cause the gums to recede, exposing the roots of the teeth. This exposure can lead to increased sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures and make the teeth more susceptible to decay. As the disease progresses, it can result in bone loss, causing the teeth to shift, loosen, or even fall out.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Gum Recession | Gums pull away from teeth, exposing roots |
| Tooth Sensitivity | Increased sensitivity to temperature changes |
| Bone Loss | Loss of bone supporting the teeth |
| Tooth Loss | Teeth may shift, loosen, or fall out |
Beyond oral health, untreated gum disease can have broader health implications. Complications such as abscesses, an increased risk of heart disease, and stroke have been linked to severe gum disease. This underscores the importance of addressing swollen gums promptly to avoid these serious health risks.
If you're experiencing symptoms, consider exploring swollen gums home remedies and consult with a dental professional to prevent further complications.
SOURCES:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24907-swollen-gums
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gingivitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354453
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21482-gum-periodontal-disease
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/in-depth/dental/art-20047475
https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/mouth/gum-disease/
Need Assistance? We’re Here to Help
We are dedicated to enhancing your dental health and well-being.
We provide personalized dental care solutions for a confident, healthy smile.
Contact us today for Professional Dental Care.

Our caring staff will help you feel relaxed and comfortable in our state of the art office. We respect your time and pledge to deliver prompt service, backed by the latest knowledge, techniques, and technology.
Email: Office@schwimmerdental.com
Tel: (848) 294-2385
Fax: (732) 899-3347
Address: 1115 Arnold Ave,
Point Pleasant, NJ, 08742
Schwimmer Dental – Website by CWS