Have an appointment? Complete the Intake Form
Chewing Over the Facts: The Relationship Between Diet and Gum Disease
Impact of Diet on Gum Health
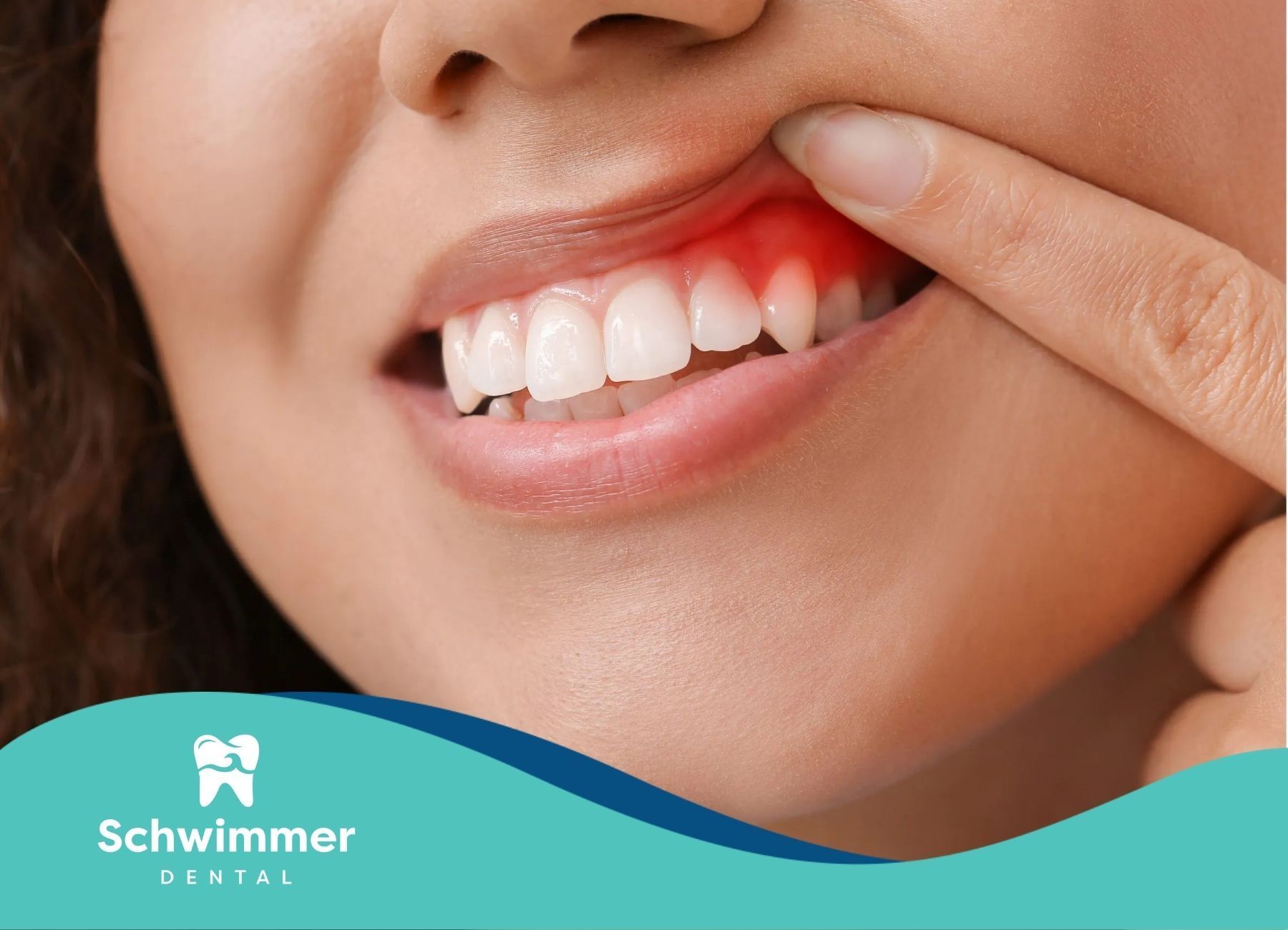
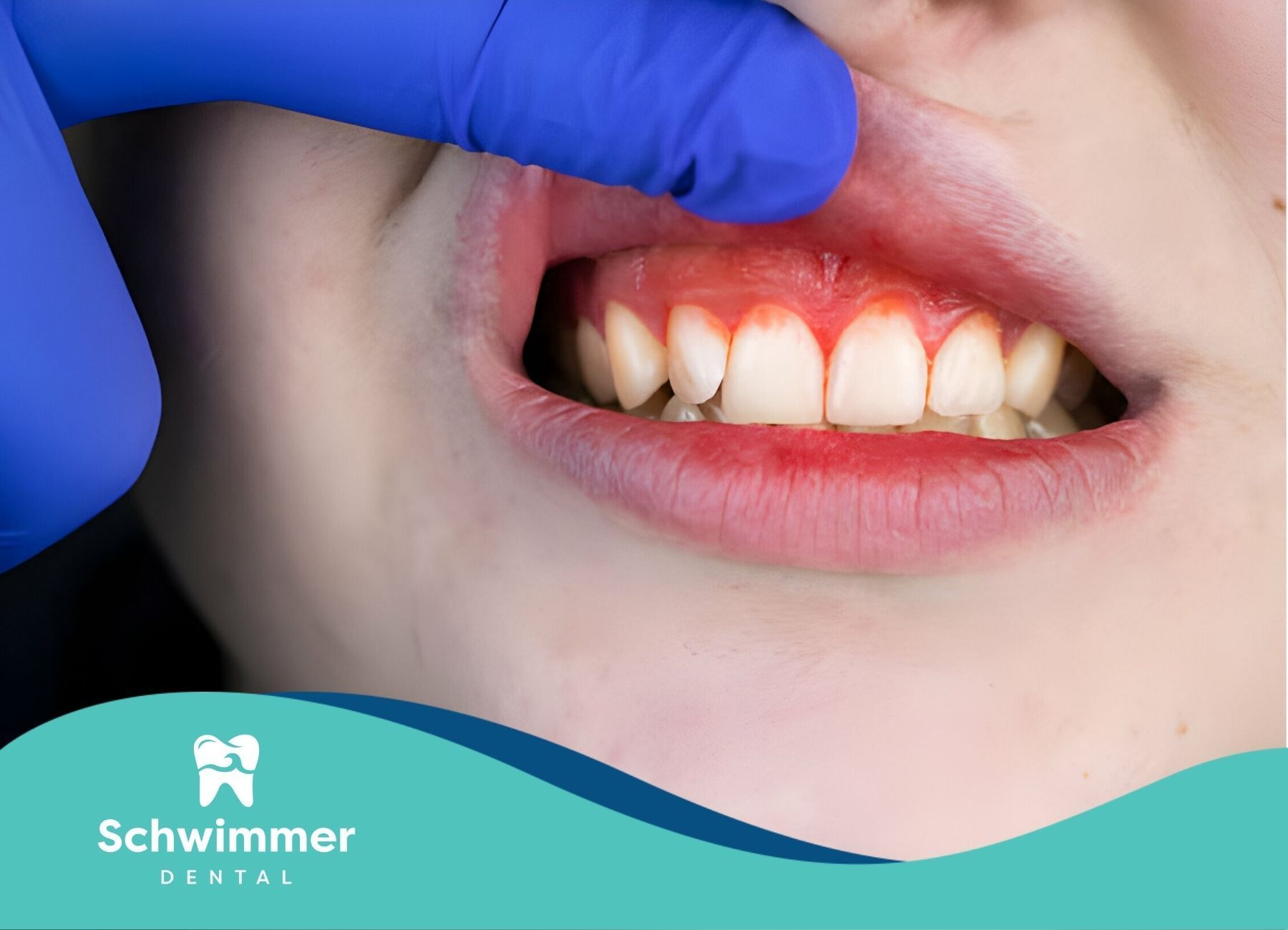
Diet plays a vital role in maintaining healthy gums and preventing gum disease. Poor nutrition can lead to the progression of gum disease, which is a major cause of tooth loss in adults. Researchers have found that a deficiency in essential nutrients can make gums more susceptible to infections, leading to more severe conditions if left untreated.
Understanding Gum Disease Progression
The progression of gum disease begins with gingivitis, which is caused by the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. If not addressed, gingivitis can escalate into periodontitis, where the inflammation spreads deeper into the supporting structures of the teeth. Certain dietary factors can accelerate this process.
Certain foods, especially those high in sugar and harmful carbohydrates, foster the growth of detrimental bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria can lead to inflammation, which can cause gums to recede over time.
Research indicates that excessive sugar intake has been linked to various health issues including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, which can all contribute to the development and worsening of gum disease. Moreover, a poor diet weakens the immune system, increasing the risk of infections and complications related to periodontal disease.
| Dietary Factor | Impact on Gum Disease |
|---|---|
| High Sugar Intake | Increases harmful bacteria growth |
| Harmful Carbohydrates | Contributes to plaque buildup |
| Acidic Foods | Enhances inflammation |
| Alcohol | Weakens the immune response |
Making dietary adjustments by avoiding foods high in sugar, starchy foods, acidic foods, and alcoholic beverages is essential for promoting oral health. Individuals should focus on a balanced diet to nourish their gums and overall dental health. For more information on maintaining a healthy diet, refer to our comprehensive guide on dental health and nutrition.
Sugary and Harmful Carbohydrate Influence
Diet greatly influences gum health. Foods high in sugar and harmful carbohydrates can promote the growth of detrimental bacteria in the mouth, leading to inflammation and potential gum recession over time. Understanding this relationship is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health.
Role of Sugar in Oral Bacteria Growth
Sugar serves as a primary energy source for harmful bacteria present in the oral microbiome. When sugar is consumed, these bacteria flourish, leading to the production of acids. These acids are damaging to teeth and gums, contributing to the development of plaque and, if not managed properly, tartar formation.
| Effect of Sugar on Oral Health | Description |
|---|---|
| Bacterial Growth | Sugar consumption fuels harmful oral bacteria, enabling them to thrive and multiply. |
| Acid Production | Bacteria convert sugars into acids, which can erode tooth enamel and irritate gum tissue. |
| Plaque Formation | Accumulation of bacteria and acids leads to plaque, which can harden into tartar if not removed. |
For more information on the specific effects of sugar on teeth, check out our article on sugar's effect on teeth.
Avoiding Foods Leading to Inflammation
To support gum health, it is advisable to minimize the intake of sugar-rich foods and harmful carbohydrates. Certain foods have been identified as particularly inflammatory and should be limited or avoided:
| Foods to Avoid | Impact on Gum Health |
|---|---|
| Sugary Snacks (candies, cookies) | Increase bacteria growth and plaque buildup |
| Soft Drinks | Acidic content damages enamel and promotes bacteria |
| White Bread | High glycemic index may contribute to inflammation |
| Processed Foods | Often high in sugars and unhealthy fats |
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for good oral hygiene. Focusing on foods that promote health can help to mitigate the risks associated with high sugar intake.
By understanding the impact of sugar and harmful carbohydrates on gum health, individuals can make informed dietary choices that support their overall dental well-being.
Strategies for Healthy Gums
Implementing a proactive approach to dietary choices is essential for maintaining healthy gums. Understanding the relationship between diet and gum disease can inform better nutritional decisions, which can ultimately lead to improved oral health.
Implementing Diet Changes
Identifying and avoiding foods rich in sugar and harmful carbohydrates can significantly enhance gum health and prevent further damage. Foods high in sugar, such as candies, pastries, and sodas, stimulate the growth of bacteria that cause plaque, which can exacerbate gingivitis—a condition characterized by inflammation of the gums.
To promote healthier gums, consider removing or reducing the following foods from your diet:
| Food Type | Effects on Gum Health |
|---|---|
| Sugary Snacks (e.g., candy) | Stimulates plaque-causing bacteria |
| Carbonated Beverages | Increases acid exposure to teeth |
| Processed Foods | Often high in sugar and unhealthy fats |
By replacing these items with healthier options, individuals can support their oral health. Include more nutrient-dense foods that help reduce inflammation and promote gum health.
Importance of Nutritious Diet and Oral Hygiene
A nutrient-rich diet is fundamental for maintaining the health of both teeth and gums. Foods packed with essential vitamins and minerals can reduce inflammation and support the structure of gum tissue. Key nutrients, such as Vitamin C, Calcium, and Iron, play vital roles in gum health.
Incorporating foods like green tea, berries, peaches, walnuts, red wine, and dark chocolate, which are rich in antioxidants, can help combat inflammation linked to periodontal disease. Additionally, consuming dairy products like cheese, milk, and plain yogurt restores minerals to teeth and helps rebuild enamel due to their calcium and phosphate content.
Beyond dietary changes, maintaining good oral hygiene is also crucial. Regular brushing and flossing, combined with a tooth-friendly diet, can lead to superior gum health. Sugarless chewing gum is another beneficial option, as it stimulates saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and neutralizes acids produced by bacteria.
By combining a nutritious diet with effective oral hygiene practices, individuals can foster better gum health and reduce the risk of gum disease. For further guidance on creating a healthier diet for your dental health, explore our resources on best diet for dental health and tooth-friendly diet choices.
Sugar and Oral Health
Understanding the link between sugar consumption and oral health is crucial for maintaining healthy gums. Excessive sugar intake directly influences the progression of gum disease, making awareness important.
Link Between Sugar and Gum Disease
Sugar plays a significant role in the development of gum disease. Research indicates that a diet high in sugar can increase the severity of gum disease and accelerate its progression. Bacteria in the mouth thrive on sugars, which leads to the production of acids. These acids contribute to plaque formation, a sticky film that can adhere to teeth and gums. Failure to manage plaque can result in tartar buildup, often leading to gum disease.
The negative effects of sugar extend beyond oral health. High sugar consumption is associated with obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. These health issues can further complicate overall dental health, as individuals with such conditions may experience increased gum inflammation and an enhanced risk of periodontal disease.
| Health Issue | Associated Risks |
|---|---|
| Gum Disease | Severe gum inflammation, tooth loss |
| Obesity | Increased risk of gum problems |
| Diabetes | Worsening gum health |
| Heart Disease | Links to periodontal complications |
Effects of Sugar on Plaque Formation
The consumption of sugar triggers the growth of oral bacteria, which leads to the production of acids that erode tooth enamel and encourage plaque buildup. If not adequately removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, making it more difficult to clean and increasing the risk of gum disease.
Recent studies show a strong correlation between high sugar diets and periodontal inflammation. Observational research has demonstrated that excessive intake of added sugars correlates positively with periodontal disease rates. Sugars consumed beyond recommended limits contribute to a higher prevalence of dental decay and inflammatory periodontal disease.
To prevent gum disease, reducing sugar intake is vital. Individuals should be aware of hidden sugars found in processed foods and beverages. Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for supporting oral health.
Nutrients for Gum Health
Maintaining healthy gums is vital for overall dental health. The nutrients consumed have a significant impact on gum health, and certain vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in preventing gum disease.
Vital Vitamins and Minerals
Various vitamins and minerals are essential for the upkeep of gum health. Here is a summary of key nutrients and their benefits:
| Nutrient | Function | Daily Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Fights infection and promotes healthy gums. Deficiencies can lead to gum bleeding and disease. Sources: citrus fruits, red peppers, broccoli. | 65-90 mg |
| Vitamin A | Maintains mucous membranes in the mouth and boosts saliva production, aiding in the cleansing of food particles and bacteria. | 700-900 mcg |
| Vitamin D | Necessary for calcium absorption and strong bones; its deficiency is linked to gum disease and tooth loss. | 600-800 IU |
| Calcium | Essential for maintaining strong teeth and bones; helps restore minerals to teeth. Sources: dairy products like cheese and yogurt. | 1,000 mg |
By integrating these vitamins and minerals into their diet, individuals can enhance their gum health and reduce the likelihood of developing gum disease.
Role of Antioxidants and Collagen Production
Antioxidants play a significant role in promoting overall gum health by helping combat oxidative stress caused by bacteria and inflammation. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, may help reduce gum inflammation and promote healing.
Collagen, a protein that provides structure to the gums, is also vital for gum health. The body requires adequate levels of vitamin C to produce collagen effectively. A diet rich in antioxidants and vitamin C can thus help support collagen production and maintain strong, healthy gums.
Choosing a diverse range of nutrient-dense foods can further support oral health.
By prioritizing these nutrients, individuals can contribute to healthier gums and a lower risk of gum disease, ultimately promoting better oral hygiene and overall health.
Dietary Recommendations for Oral Health
Foods to Avoid for Healthy Gums
Certain foods can significantly impact gum health and contribute to the progression of gum disease. Research suggests that poor nutrition may lead to more severe forms of gum disease and is a major contributor to tooth loss in adults.
It's important to avoid or limit the intake of the following:
| Food Types | Reason to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Sugary Snacks | Foster the growth of harmful bacteria that can lead to gum inflammation and decay. |
| Soft Drinks | High sugar content promotes plaque buildup and acid attacks on teeth. |
| White Bread and Pasta | Made with refined carbohydrates, these foods can break down into sugars in the mouth. |
| Candy and Sweets | Induce prolonged exposure to sugar, which can lead to tooth decay and gum issues. |
| Processed Foods | Often high in sugars and low in nutrients, contributing to poor gum health. |
Consuming a balanced diet that avoids these foods can help maintain healthier gums and overall dental health.
Importance of Hydration and Snacking Habits
Hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health. Water helps in washing away food particles and bacteria, which can reduce plaque buildup and the risk of gum disease. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially after meals.
Moreover, snacking habits can also affect gum health. Choosing tooth-friendly snacks helps support healthy gums. Here are some beneficial snack options:
| Healthy Snack Options | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Fruits (e.g., apples, pears) | High in fiber, aiding in cleaning teeth and stimulating saliva production. |
| Vegetables (e.g., carrots, cucumbers) | Crunchy textures help clean teeth and gums. |
| Nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts) | Provide nutrients and are low in sugar, beneficial for gum health. |
| Cheese | Contains calcium, which strengthens teeth and helps neutralize acids. |
Improving hydration and making healthy snacking choices can contribute to better gum health and reduce the risk of developing gum disease.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining a balanced diet not only benefits your overall health but also plays a crucial role in keeping your gums healthy and preventing gum disease. By making informed dietary choices, you can reduce the risk of inflammation, plaque buildup, and other gum-related issues.
Take the first step towards better oral health today—schedule your next dental checkup with Schwimmer Dental. Let us help you keep your smile healthy and vibrant!
Resources:
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5133084
- https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=1&contentid=4062
- https://www.mouthhealthy.org/all-topics-a-z/diet-and-dental-health
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41405-024-00265-w
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325873
Need Assistance? We’re Here to Help
We are dedicated to enhancing your dental health and well-being.
We provide personalized dental care solutions for a confident, healthy smile.
Contact us today for Professional Dental Care.

Our caring staff will help you feel relaxed and comfortable in our state of the art office. We respect your time and pledge to deliver prompt service, backed by the latest knowledge, techniques, and technology.
Email: Office@schwimmerdental.com
Tel: (848) 294-2385
Fax: (732) 899-3347
Address: 1115 Arnold Ave,
Point Pleasant, NJ, 08742
Schwimmer Dental – Website by CWS