Have an appointment? Complete the Intake Form
Eat Your Way to Healthy Teeth: Best Diet for Dental Health
Impact of Diet on Dental Health
Diet's Role in Tooth Decay
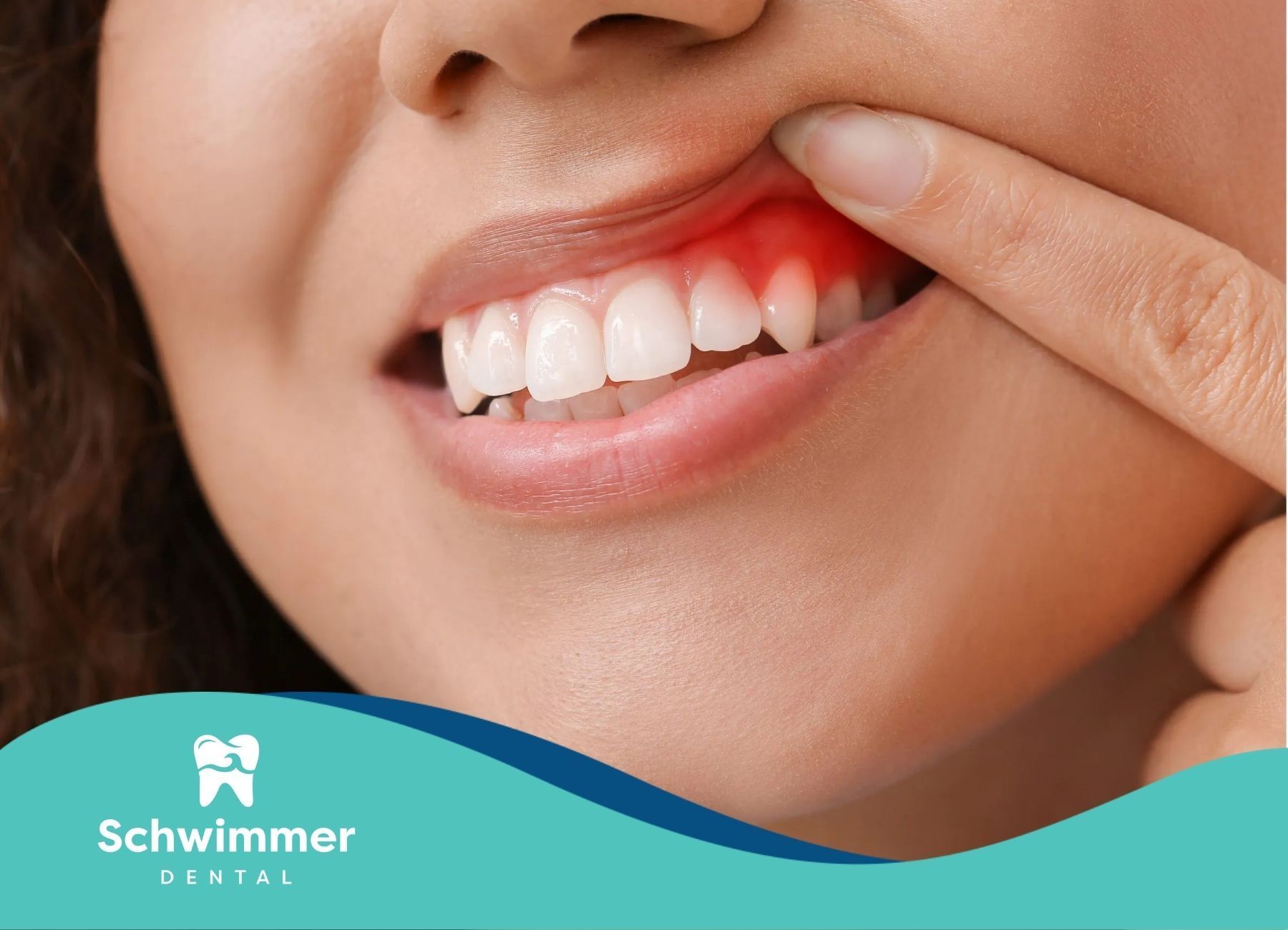
Diet plays a significant role in maintaining dental health. Certain foods and beverages can contribute to tooth decay by fostering an environment where harmful bacteria thrive. One of the most concerning dietary components is sugar.
Sucrose, the most common dietary sugar, is considered the most cariogenic carbohydrate, increasing the risk of dental caries. This sugar serves as a critical food source for plaque bacteria found in the mouth, which contributes to enamel erosion and tooth demineralization. When these bacteria metabolize fermentable carbohydrates like sucrose, they produce acids that can damage tooth enamel and lead to cavities.
Dental caries occur when the demineralization of the enamel surpasses its ability to remineralize. The balance between these two processes is disrupted primarily due to bacterial activity in dental plaque. It is estimated that tooth decay affects about 1 in 3 adults and close to 1 in 4 children in the UK. Despite improvements in oral health over the years, tooth decay remains one of the most prevalent oral health issues, second only to the common cold.
Food adhesion is also a critical factor in tooth decay. The stickiness of certain foods, particularly sugary snacks, directly correlates to their cariogenic potential. More adherent foods can remain on the tooth surfaces longer, giving bacteria more time to produce harmful acids.
| Dietary Component | Impact on Teeth |
|---|---|
| Sucrose | Increases risk of dental caries |
| Sticky Foods | Promotes plaque retention |
| Acidic Foods | Erodes enamel |
For a comprehensive understanding of how different foods affect dental health, consider exploring the connections between dental health and nutrition and discover tooth-friendly diet choices. It's essential to be aware of how diet influences oral health, as sugar's effect on teeth can lead to long-term issues if not managed properly. Understanding the interplay between dietary habits and gum health is equally important.
Harmful Foods for Teeth
Diet plays a significant role in maintaining dental health, and certain foods can have detrimental effects on teeth. Understanding which foods to limit can help individuals make better choices for their oral hygiene. This section will focus on two harmful categories: sugary and acidic foods, and sticky and hard foods.
Sugary and Acidic Foods
Sugary foods are particularly problematic for dental health. Sucrose, the most common dietary sugar, is highly cariogenic, meaning that it increases the risk of dental caries or cavities. Frequent consumption of simple sugars leads to increased acid production by bacteria in the mouth, which can demineralize tooth enamel. Every time sugar is consumed, the risk of enamel demineralization rises, especially with frequent intake.
Acidic foods and drinks also contribute to dental erosion. Items such as coffee, sodas, energy drinks, tomatoes, and citrus fruits can weaken tooth enamel over time. It is advisable to rinse the mouth after consuming these foods to mitigate their effects. Additionally, consuming acidic items as part of a meal may lessen their impact compared to eating them alone.
| Food Category | Examples | Effects on Dental Health |
|---|---|---|
| Sugary Foods | Candies, pastries, sodas | Increases risk of cavities |
| Acidic Foods | Coffee, citrus fruits | Erodes tooth enamel |
Sticky and Hard Foods
Sticky foods pose a unique risk to dental health due to their tendancy to adhere to tooth surfaces. The stickiness of these foods can increase their cariogenic potential, as they may remain in the mouth longer, giving bacteria more time to produce acids that damage tooth enamel. Common sticky foods include gummy candies, caramels, and even some granola bars that can cling to teeth.
On the other hand, hard foods—including certain nuts and hard candies—can physically damage teeth. Biting down on hard objects can lead to cracks or fractures in the enamel, making the teeth more susceptible to decay and sensitivity.
| Food Category | Examples | Effects on Dental Health |
|---|---|---|
| Sticky Foods | Gummy candies, granola bars | Increases risk of cavities |
| Hard Foods | Nuts, hard candies | Can cause cracks or fractures in teeth |
Being mindful of these harmful food categories can help individuals maintain a healthier smile.
Beneficial Foods for Dental Health
Maintaining dental health is closely linked to the foods consumed. Certain foods play a significant role in strengthening teeth and promoting overall oral health. This section discusses two key categories of beneficial foods: sources of calcium and vitamin D, as well as saliva-stimulating foods.
Calcium and Vitamin D Sources
Calcium and vitamin D are essential nutrients for dental health. Calcium helps harden tooth enamel and strengthens the jawbone, making it crucial for preventing tooth decay. Good dietary sources of calcium include:
| Food Item | Calcium Content (mg) |
|---|---|
| Milk (1 cup) | 300 |
| Cheese (1 oz) | 200 |
| Yogurt (1 cup) | 400 |
| Broccoli (1 cup) | 47 |
| Salmon (3 oz) | 181 |
Vitamin D, on the other hand, enhances calcium absorption and boosts bone mineral density. It can be found in:
| Food Item | Vitamin D Content (IU) |
|---|---|
| Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, 3 oz) | 570 |
| Canned tuna (3 oz) | 154 |
| Fortified milk (1 cup) | 100 |
| Portabello mushrooms (1 serving) | 400 |
Sources for vitamin D include fatty fish, portabello mushrooms, fortified foods, and exposure to sunlight. Foods rich in calcium and vitamin D, such as dairy products and fatty fish, contribute to building strong teeth and preventing enamel erosion. Dairy products like cheese, milk, and plain yogurt also provide phosphates that help remineralize teeth.
Saliva-Stimulating Foods
Saliva plays a vital role in dental health by washing away food particles and neutralizing acids produced by bacteria in the mouth. Certain foods can stimulate saliva production, aiding in the protection against cavities. Fruits and vegetables, especially those that are crunchy and high in water content, are excellent choices.
Fruits like apples, pears, and celery are beneficial as they not only promote saliva flow but also contain fibers that help clean teeth as they are eaten. Incorporating these foods into one’s diet can enhance overall dental health.
Besides cleaning teeth and gums, these foods provide essential vitamins such as vitamin C and vitamin A, which are important for maintaining healthy gums and mitigating gum disease.
Today’s best diet for dental health can be supported by selecting tooth-friendly options.
Optimal Dietary Habits
Maintaining optimal dietary habits is essential for promoting dental health and preventing cavities and other oral issues. Two key aspects of these habits include limiting sugar intake and ensuring proper hydration.
Limiting Sugar Intake
Limiting sugar intake is crucial for sustaining healthy teeth. The World Health Organization (WHO) advises that individuals should keep their sugar consumption to less than 10% of total dietary intake, ideally aiming for 5% to effectively prevent cavities. High sugar consumption provides a food source for plaque bacteria, which contributes to enamel erosion and tooth demineralization, ultimately leading to tooth decay.
The frequency of sugar intake also plays a significant role in dental health. Enamel is demineralized each time sugar is consumed, and the demineralization process intensifies with frequent sugar consumption. A systematic review by WHO confirmed that the amount and frequency of sugar consumed is directly linked to the development of dental caries.
| Sugar Intake Level | Recommended Percentage of Energy Intake | Dental Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 5% | Optimal for preventing cavities | Low risk of dental caries |
| 5% - 10% | Moderate risk of dental caries | Increased risk of tooth decay |
| Over 10% | High risk of dental caries | Significant enamel erosion |
For individuals aiming for a tooth-friendly diet, choosing sugarless alternatives, such as sugar-free gum, can stimulate saliva production, which aids in removing food particles and bacteria.
Importance of Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is another vital aspect of good dental health practices. Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria from the mouth, preventing plaque buildup. Additionally, proper hydration helps combat dry mouth, which can reduce the risk of tooth decay and oral infection.
Water not only supports overall bodily functions but also promotes the health of your teeth and gums. For optimal results, individuals should prioritize water consumption throughout the day, particularly after meals.
In summary, incorporating healthy dietary habits by limiting sugar intake and maintaining hydration are essential components of the best diet for dental health. By following these practices, individuals can significantly improve their oral health and reduce the risk of dental issues.
Key Nutrients for Teeth
A healthy diet plays a significant role in maintaining dental health. Certain nutrients are particularly beneficial for strengthening teeth and gums. In this section, we will explore key nutrients such as calcium, phosphorus, potassium, vitamin C, and vitamin D, which contribute to the overall health of an individual's oral cavity.
Calcium, Phosphorus, and Potassium
Calcium is essential for dental health as it helps harden tooth enamel and strengthens the jawbone. Here are some good sources of calcium:
| Calcium Sources | Examples |
|---|---|
| Dairy Products | Milk, cheese, yogurt |
| Vegetables | Broccoli, carrots |
| Fish | Salmon |
Phosphorus works in conjunction with calcium to form hydroxyapatite, the main mineral component of both bones and tooth enamel. Sources of phosphorus include:
| Phosphorus Sources | Examples |
|---|---|
| Seafood | Fish, shellfish |
| Meat | Beef, pork |
| Legumes | Soybeans, lentils |
Potassium improves bone mineral density and helps prevent acid buildup in the body, which can strip calcium from bones and teeth. Good sources of potassium include:
| Potassium Sources | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fruits | Bananas, avocados |
| Vegetables | Swiss chard, tomatoes |
| Tubers | Potatoes, sweet potatoes |
Vitamin C and Vitamin D
Vitamin C is vital for maintaining gum health. It strengthens gums and soft mouth tissue, protects against gingivitis, and prevents teeth from loosening. Food sources rich in vitamin C include:
| Vitamin C Sources | Examples |
|---|---|
| Citrus Fruits | Oranges, lemons |
| Vegetables | Potatoes, leafy greens |
Vitamin D is crucial for oral health as it helps the body absorb calcium and boosts bone mineral density. Key dietary sources of vitamin D include:
| Vitamin D Sources | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fatty Fish | Salmon, canned tuna |
| Fortified Foods | Milk, orange juice, cereals |
| Other Sources | Portobello mushrooms, sunlight exposure |
Societal Factors in Oral Health
Oral health is influenced by several societal factors, particularly socioeconomic status and hospitalization rates due to tooth decay. These elements impact access to dental care, nutrition, and overall health, illustrating the importance of addressing societal disparities in oral health.
Socioeconomic Influence
Individuals from lower-income households are more likely to suffer from dental caries compared to those from higher-income households. According to Action on Sugar, adults with lower incomes have a higher prevalence of dental caries (37%) than those from higher-income households (26%). This disparity illustrates how social factors impact oral health, where financial limitations can restrict access to necessary dental care and healthy food options, often leading to poor dietary choices that further harm dental health.
The nutritional quality of a diet plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health. Malnutrition, stemming from either overeating or undereating, can lead to complications like dental pain, difficulty chewing, and an increased risk of oral diseases. Proper nutrition is essential for the development and maintenance of healthy teeth and gums. Poor oral health can also exacerbate general health conditions, highlighting the need for a well-rounded diet that contributes to overall health.
Hospitalizations due to Tooth Decay
Tooth decay remains a significant public health issue, especially among children. In the UK, approximately 26,000 children aged 5-9 years are hospitalized each year due to tooth decay, which averages to around 500 hospitalizations each week. This makes tooth decay a leading cause of hospitalization for this age group. Such high rates of hospitalization can be attributed to a combination of factors, including poor dietary habits, lack of access to dental care, and insufficient education on maintaining oral health.
Tooth decay affects not just individuals but society as a whole, leading to increased healthcare costs and loss of productivity. Preventing tooth decay through a tooth-friendly diet choices and promoting good oral hygiene practices are essential steps in reducing these hospitalization rates and improving overall public health. Additionally, the connection between diet and dental health is critical to understanding how dietary habits can either safeguard or jeopardize oral health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the foods and beverages we consume have a profound impact on our dental health. By making conscious dietary choices—such as limiting sugar, avoiding sticky and acidic foods, and incorporating tooth-friendly nutrients like calcium and vitamin D—you can help protect your teeth and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile.
Ready to take your dental care to the next level? Schedule your appointment with Schwimmer Dental today, and let us help you achieve optimal oral health!
Resources:
- https://www.actiononsugar.org/sugar-and-health/sugars-and-tooth-decay/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534248/
- https://www.who.int/
- https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=1&contentid=4062
- https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/oral-health/
Need Assistance? We’re Here to Help
We are dedicated to enhancing your dental health and well-being.
We provide personalized dental care solutions for a confident, healthy smile.
Contact us today for Professional Dental Care.

Our caring staff will help you feel relaxed and comfortable in our state of the art office. We respect your time and pledge to deliver prompt service, backed by the latest knowledge, techniques, and technology.
Email: Office@schwimmerdental.com
Tel: (848) 294-2385
Fax: (732) 899-3347
Address: 1115 Arnold Ave,
Point Pleasant, NJ, 08742
Schwimmer Dental – Website by CWS